The Costs and Benefits of Liquidity Regulations: Lessons from an Idle Monetary Policy Too
Christopher J Curfman, John Kandrac
Review of Finance, Volume 26, Issue 2, March 2022, Pages 319–353, https://doi.org/10.1093/rof/rfab024
Liquidity regulations implemented after the global financial crisis had a transformative effect on the financial system. The rapid implementation of such regulations occurred despite the relatively limited empirical evidence on the effects of liquidity requirements on banks. The simultaneous introduction of other bank regulations after the financial crisis frustrate attempts to measure the effects of more recent liquidity requirements.
In this paper, we examine the possible costs and benefits of mandated bank liquidity buffers by exploring the effects of a reserve requirement, which is de facto liquidity requirement that was in place in the United States in the years before the financial crisis. Although reserve requirements were not altered following the de-emphasis on monetary aggregates to pursue monetary policy objectives, the required reserve schedule increases sharply beyond an exogenous asset threshold.
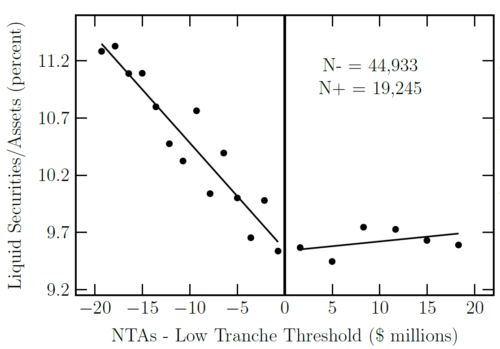
The kink in the reserve requirement schedule allows us to draw causal inference using a regression kink design. We find that a higher liquid asset requirement led banks to substitute out of the most illiquid types of loans and into cash and other assets with higher liquidity value. Banks passed on only some of the cost of the liquidity requirement to depositors, causing bank profits to fall.
Finally, we document a microprudential benefit of liquidity requirements by demonstrating that banks with higher cash requirements prior to the financial crisis had a lower probability of failure. The beneficial effects of liquidity requirements on bank survival apparently stem from both a reduction in risky commercial loan intensity and a lower likelihood that banks with higher liquidity requirements will be forced to sell distressed securities amid fire sales. Our results offer a unique perspective on the causal effects of liquidity regulations and yield several general lessons for policymakers regarding the costs and benefits of such regulations.
Figure 1