Nikolaus Hautsch, Christoph Scheuch, Stefan Voigt
Review of Finance, Volume 28, Issue 4, July 2024, Pages 1345–1381, https://doi.org/10.1093/rof/rfae004
This paper examines the impact of counterparty risk and settlement latency on the trading of blockchain-based assets in the context of centralized exchanges (CEX). We contrast traditional stock markets, which rely on trusted intermediaries like central clearing counterparties to mitigate counterparty risk, with blockchain technology’s promise to eliminate the need for such intermediaries through a network of validators reaching consensus on transaction histories.
CEXes, which handle the majority of crypto token transactions, offer fast and efficient trading by settling transactions off-chain, albeit at the risk of exposing traders to the default risk of exchanges.
We show that settlement latency—the delay until a transaction is validated on the blockchain—poses significant costs to cross-exchange arbitrageurs, who exploit price differences across exchanges. This latency exposes arbitrageurs to price risk, making arbitrage opportunities viable only if the price differences are substantial enough to offset this risk. We derive a closed-form expression for the arbitrageur’s certainty equivalent. The certainty equivalent increases with expected and variance of settlement latency, price volatility, and the arbitrageur’s risk aversion.
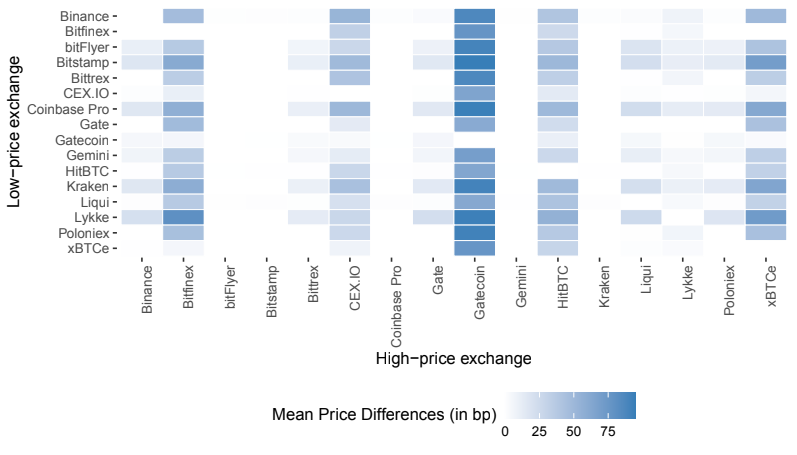
Our empirical analysis, utilizing minute-level data from 16 large CEXes and high-frequency Bitcoin network information, supports the theoretical framework. It reveals that substantial price differences across exchanges coincide with periods of high settlement latency, high latency uncertainty, and high spot volatility. We examine the mitigating role of trust in reducing cross-exchange arbitrage costs, evidenced by narrower price differences between CEXes with larger funds under custody.
We believe our paper contributes to understanding the economic implications of blockchain technology for financial market trading, highlighting a specific friction arising from the effort to mitigate counterparty risk for blockchain-based assets. Settlement latency represents a severe economic friction. Bypassing this friction requires re-installing core components of trusted intermediation, with all associated costs and risks.